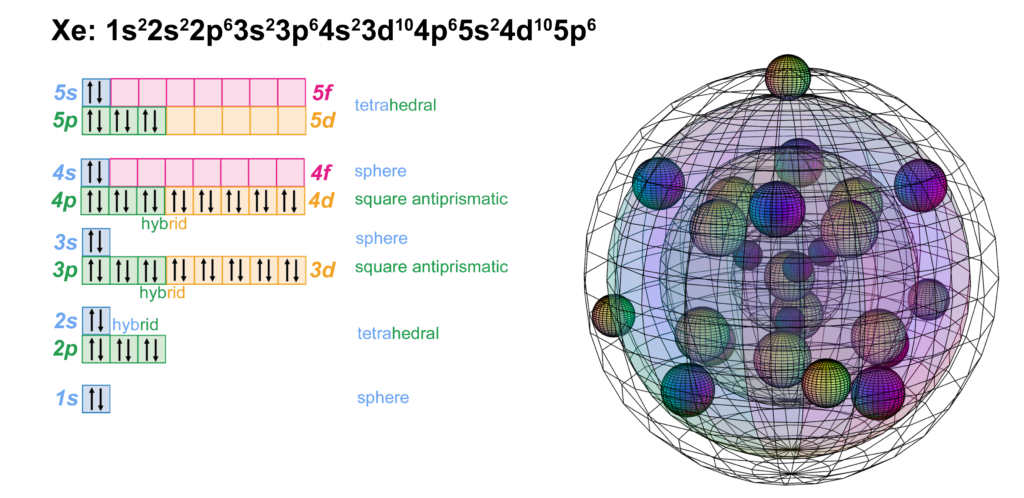
RETURN to Periodic Table
Xenon is the sixth element with electrons in the 5p orbital. Xenon has five full shells. Like neon, argon, and krypton, it achieves symmetrical stability without the need to hybridize its 5s and 5p orbitals. It is not as unreactive as the other noble gases since its larger size means its electrons are further from and less well-bound to the nucleus. This lowers ionization energy to the point that it can bond with, for example, the electronegative oxygen and fluorine atoms. (The wireframe indicates the boundary of the n=5 shell.)
 CLICK HERE to interact with this object
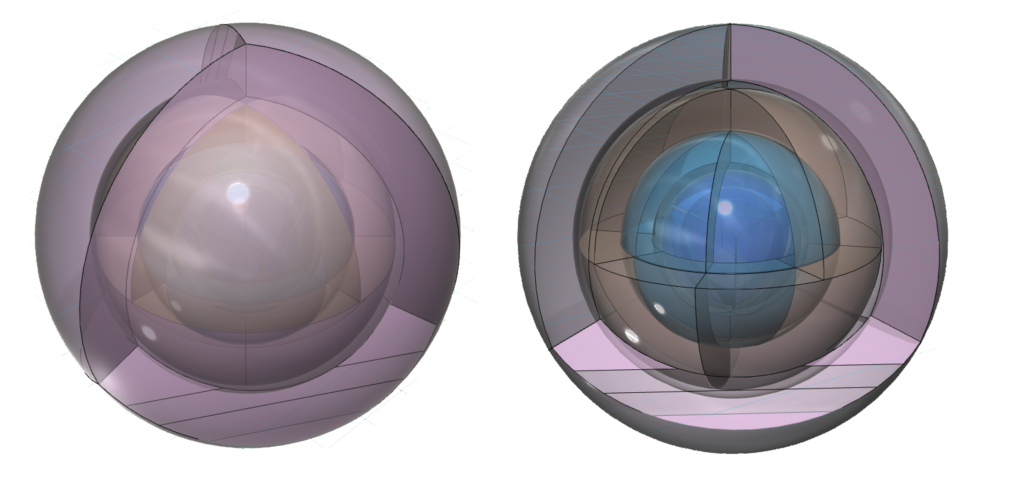
CLICK HERE to interact with this objectAn alternate view (shown below) of the orbitals of xenon shows an innermost 1st-shell sphere within a 2nd tetrahedral shell (dark blue) within a 3rd cubic anti-prismatic shell (light blue) within an anti-aligned 4th cubic anti-prismatic shell (brown) within a 5th tetrahedral shell (pink).
RETURN to the Periodic Table
SEE OTHER NOBLE GASES: Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon